What is the Dow Jones Industrial Average? (DJIA) Everything You Need to Know
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA), often simply referred to as "the Dow," is a hallmark of the U.S. stock market, focusing predominantly on blue-chip companies. Established in 1896, the DJIA is an index of 30 major U.S. companies from various sectors, ranging from tech to financials.
Decoding the Dow
The DJIA provides a snapshot of the broader U.S. economy, showcasing how leading industries fare. It is a price-weighted index, meaning the stock prices directly influence the Dow's value, unlike the market-capitalization-weighted indices like the S&P 500 and the Nasdaq.
The Dow's value is calculated using a divisor that accounts for stock splits and other adjustments, ensuring continuity. It's a gauge of the stock prices of its components, making it sensitive to price changes in high-priced stocks.
How to Invest in the Dow Jones
Though one cannot invest directly in the DJIA, ETFs like the SPDR Dow Jones Industrial Average ETF (DIA) provide an avenue for investors to mirror its movements. DIA can be conveniently purchased through brokerage accounts.
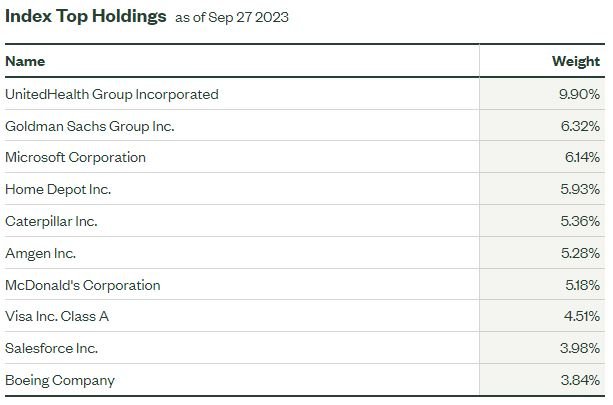
Which Stocks are in the Dow Jones Index?
The DJIA's 30 components are dynamic, with occasional changes reflecting the evolving business landscape. These include stalwarts like UnitedHealth (UNH), Microsoft (MSFT), and Goldman Sachs (GS). Check out the Dow Jones’ top 10 holdings below for a clearer picture. As you can see, UNH stock carries the biggest weighting at 9.9%, meaning that for every $100 you invest, $9.90 would go toward UNH.
Dow Jones Top Holdings. Source: State Street Global Advisors
Below, you can see that the Dow Jones gives you heavy exposure to healthcare, financials, and information technology stocks while also being diversified into other sectors.
Source: State Street Global Advisors
The Dow and Its Counterparts
While the DJIA concentrates on 30 significant firms, there are other indices as well, like the S&P 500, which captures a broader spectrum of the U.S. market, including 500 major U.S. companies. The Nasdaq index, meanwhile, is tech-centric, encompassing firms listed on the Nasdaq stock exchange.
Dominated by the tech industry, the Nasdaq boasts a wider array of companies. Check out our Nasdaq overview for more insights.
S&P 500: With a broad market scope, the S&P 500 includes top U.S. entities across sectors. Discover more about the S&P 500 here.
Russell Indices: Highlighting mostly smaller firms, these indices, like the Russell 2000, give a glimpse into smaller-cap companies.
Potential Pitfalls of the Dow
Due to its price-weighting methodology, the Dow can be heavily influenced by high-priced stocks. It does not always reflect the broader market sentiment, making it crucial for investors to consult other indices for a comprehensive perspective.
Concluding Remarks
The Dow Jones Industrial Average, with its century-old legacy, offers a unique lens to view the U.S. market's pulse. As economies evolve and industries adapt, understanding the intricacies of indices like the DJIA becomes indispensable for informed investors.